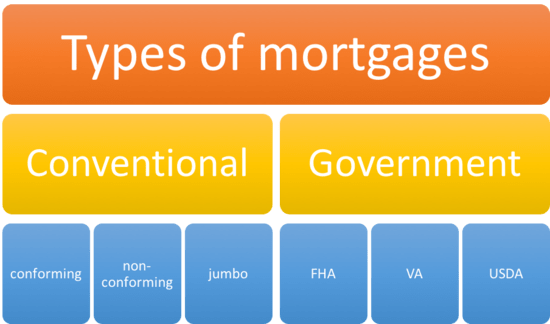
Getting a mortgage to buy a home is one of the biggest financial decisions you’ll make When exploring your options, you’ll likely come across conventional loans These are mortgages issued by private lenders, rather than government entities.
Conventional loans make up the majority of mortgages originated today. In fact, according to Urban Institute, conventional conforming loans accounted for 448% of all mortgages in Q4 2023
If you’re considering a conventional mortgage, it helps to understand the different types available. Here are four of the most common conventional loan varieties.
1. Conforming Conventional Loans
The most popular subtype of conventional loan is the conforming conventional mortgage. These adhere to limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, two government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs).
The conforming loan limit changes annually. For 2024 it’s $726200 for most of the U.S. Higher limits exist for certain high-cost areas like New York City or San Francisco.
Conforming conventional loans offer several benefits:
-
Low rates: Since they can be purchased by Fannie and Freddie, conforming loans provide lenders with capital to originate more mortgages. This steady funds flow lets them offer lower interest rates.
-
Flexible credit requirements: While conforming conventional loans do have standards, they aren’t as strict as some loan programs. For example, you may only need a 620 credit score versus 640 for certain government-backed mortgages.
-
Low down payments: Many lenders allow down payments as low as 3% on conforming conventional loans. This makes them more affordable for first-time homebuyers.
-
No geographic restrictions: Conforming conventional loans can be used to finance homes anywhere in the U.S. and its territories. Some special mortgage programs limit you to certain rural or suburban areas.
As you can see, conforming conventional loans offer a nice middle ground. They provide flexible options without being too restrictive or requiring pristine credit.
2. Non-Conforming Conventional Loans
What if you need to borrow more than the conforming loan limit? Or maybe you don’t quite meet the standards for a conforming conventional mortgage?
In those cases, a non-conforming conventional loan may work. As the name implies, these fall outside conforming guidelines set for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
There are a few common types of non-conforming conventional loans:
-
Jumbo loans – For high-cost areas, jumbo mortgages let you borrow more than the conforming limit. Down payments are typically 10-20%.
-
Portfolio loans – Banks may keep these mortgages on their own books instead of selling to Fannie/Freddie. This provides more flexible underwriting.
-
Non-QM loans – Short for non-qualified mortgages, these are for borrowers who fall outside typical affordability metrics. They usually have higher rates.
While non-conforming loans offer more options, you’ll likely pay a price in terms of higher interest rates, larger down payments, or stricter eligibility.
3. Fixed-Rate Conventional Loans
Mortgages fall into two categories based on their interest rate: fixed or adjustable. The most popular conventional loans have a fixed rate.
With a fixed-rate mortgage, your interest rate stays the same for the entire repayment term. Whether you choose a 15-year or 30-year loan, your principal and interest payment will never change.
Fixed-rate conventional loans offer stability. You don’t have to worry about rising interest rates increasing your payment like you would with an adjustable-rate mortgage.
Most fixed-rate conventional loans are fully amortized. This means your payment pays down a portion of the principal each month. As you make payments over time, more goes toward principal and less toward interest.
The downside is that fixed-rate mortgages may have higher rates than adjustable-rate mortgages. However, for many homebuyers, the rate security is worth the small premium.
4. Adjustable-Rate Conventional Loans
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) are the other main type of conventional loan. With an ARM, you’ll have an introductory interest rate for the first 3, 5, 7, or 10 years of the loan.
After the initial fixed-rate period, the interest rate can change annually. It’s tied to an index like the prime rate or LIBOR.
Here are some quick pros and cons of ARMs versus fixed-rate conventional loans:
Pros
- Lower initial rates
- Potentially pay off mortgage faster
Cons
- Payment may increase substantially after intro period
- Difficult to budget with fluctuating payment
In most cases, an ARM makes sense if you plan to move before the intro rate expires. This way, you can take advantage of lower initial rates without the risk of payment spikes down the road.
However, if you want to stay in your home long-term, a fixed-rate conventional loan provides stability. Even if an ARM payment stays the same, it likely won’t go down much either.
How to Choose the Right Conventional Loan
When picking a conventional mortgage, consider the following:
-
Your budget – Make sure your income, debts, and down payment align with loan requirements. Non-conforming loans offer more flexibility if you don’t meet conforming standards.
-
How long you’ll stay – Fixed-rate mortgages are better for long-term homeowners. ARMs can save money in the short run if you plan to move sooner.
-
Your risk tolerance – If you prefer predictability and can afford somewhat higher rates, a fixed-rate mortgage may suit you best.
-
Your home value – In high-cost areas, jumbo loans let you borrow above conforming limits. Or you may prefer a conforming loan to access better rates.
While shopping, get rate quotes from multiple lenders. Compare estimated monthly payments and closing costs to find your best deal.
Key Takeaways on Conventional Mortgage Types
Conventional loans from private lenders represent the majority of mortgages originated today. Within the conventional loan category, you’ll find:
-
Conforming loans – Meet standards for purchase by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Offer competitive rates and flexible guidelines.
-
Non-conforming loans – Exceed conforming limits or guidelines. May have higher costs but provide more options.
-
Fixed-rate mortgages – Interest rate and payment stay the same over the loan term. Provide predictability.
-
Adjustable-rate mortgages – Interest rate adjusts periodically after an introductory period. Offers lower initial rates but unpredictable long-term costs.
Which type of conventional loan works best depends on your budget, credit, down payment, and plans for the home. Compare multiple lenders to find the right financing option at the lowest cost.
Types of Conventional Loans & How They Work
A conventional loan is one that is not backed or insured by an agency of the federal government. There are two types of conventional mortgage loans, conforming and non-conforming. Telling them apart can be kind of tricky, so we’ll outlines the differences and what you need to know to choose the mortgage that’s best for you. At Credit Union of Southern California (CU SoCal), we make getting a mortgage easy! Call 866.287.6225 today to schedule a no-obligation consultation and learn about our home equity lines of credit, auto loans, personal loans, checking and savings accounts, and other banking products. As a full-service financial institution, we look forward to helping you with all of your banking needs. Read on to larn more about types of conventional mortgage loans!
Advantages of Conventional Loans
- Faster Loan Underwriting. Because conventional loans have standard requirements, they are easier for the lender to process and approve.
- More Options. Borrowers have more options, including 15, 20, or 30-year loans.
- Optional Escrow Accounts. Most new mortgages require that money be set aside in an escrow account for payment of the homeowners insurance and property tax. These amounts are included in the monthly mortgage payment. Not only is this convenient for the borrower, it reduces risk for the lender. Some lenders will allow the borrower to pay their own homeowners insurance and property tax if there is a 20% down payment on the original transaction or the borrower reaches 20% equity in their home.
- Security. Most conventional loans have a fixed interest rate, so borrowers can be secure knowing how much their monthly payments will be.
- Can Be Used on All Property Types. Whether you’re buying a house or condominium, a conventional loan can get the deal done.
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) May Not Be Required. For buyers who can make a down payment of more than 20%, PMI may be waived by the lender.
Types of Mortgages: VA, FHA & Conventional | Real Estate Exam Prep
FAQ
What is the most common conventional mortgage?
What is a 5 down conventional loan?
Do lenders prefer FHA or conventional?
What is a conforming conventional loan?
A conforming conventional loan is the most common type of conventional loan, which conforms to the guidelines set by the Federal Housing and Finance Agency (FHFA). Conventional loans are also available as fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, jumbo, and non-qualifying mortgages.
What is a conventional mortgage?
Conventional loans are simply mortgages that aren’t backed by government entities like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) or U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Homebuyers who can qualify for conventional loans should strongly consider this type of loan, as it’s likely to provide less costly borrowing options.
Are there different types of conventional loans?
There are more than one type of conventional loan. Conventional loans are a popular mortgage option, even for first-time home buyers. Keep reading to learn more about the main types of conventional mortgage products and what their differences might mean for you. What is a conventional home loan?
Are conventional mortgages government-backed?
Conventional mortgages are not government-backed, unlike USDA or FHA loans. However, to qualify as a conventional mortgage, the loan must comply with lending rules set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. These rules do not require government backing. The loan limit for conventional mortgages varies by location. For 2020, the limit in most areas is $510,400.
