When buying a home, you’ll likely work with a lender and a loan officer at some point in the mortgage process. But what exactly do these professionals do, and how are their roles different? Understanding the key distinctions can help you know what to expect when applying for a mortgage loan.
Mortgage Lenders
Mortgage lenders are financial institutions that offer mortgage loans directly to borrowers. Examples include banks, credit unions, and other lending institutions.
The primary role of a mortgage lender is to lend money for home purchases They originate mortgage loans, evaluate loan applications, underwrite and approve loans, fund loans at closing, and service loans until they are paid off
Mortgage lenders have several key responsibilities:
- Offering a variety of mortgage loan options, including conventional, FHA, VA, jumbo, and more
- Reviewing borrowers’ credit reports, income, assets, and other information to assess creditworthiness
- Determining if a borrower qualifies for a particular loan program based on the lender’s requirements
- Managing the loan process from application through closing
- Providing disclosures and documentation for the loan
- Funding approved loans at closing
- Servicing the mortgage by collecting payments, handling escrow accounts, and responding to customer service issues
The loan options a mortgage lender can provide depend on the type of loans the institution offers. For example, some lenders specialize in VA loans for veterans or USDA loans for rural borrowers. Others focus on jumbo mortgages above conforming loan limits.
Mortgage lenders earn money through interest payments on the loans, as well as fees charged to borrowers like origination fees and discount points.
Loan Officers
Mortgage loan officers are employed by lending institutions to interact with borrowers, process mortgage applications, and guide loans through to closing.
Loan officers act as a main point of contact between borrowers and lenders. Their primary role is to originate mortgages on behalf of their lending institution.
Key responsibilities of loan officers include:
- Meeting with prospective borrowers to discuss loan options and prequalify borrowers
- Collecting documentation and information from borrowers to complete mortgage applications
- Analyzing borrowers’ financial profiles, including income, assets, credit, and debts
- Determining the loan type and loan amount borrowers may qualify for
- Educating borrowers about the mortgage process and different loan programs
- Submitting completed applications to underwriting for approval
- Serving as the main contact for borrowers throughout the lending process
- Providing loan status updates and responding to borrowers’ questions
- Facilitating the loan closing process
Loan officers usually work on salary plus commission. Their commission depends on the dollar amount of loans they originate as well as conversion metrics like the percentage of leads that turn into closed loans.
Key Differences Between Lenders and Loan Officers
While lenders and loan officers play interrelated roles in the mortgage process, there are some key ways in which their responsibilities differ:
-
Employer: Loan officers work for lending institutions, while lenders actually provide the financing.
-
Duties: Lenders focus on big-picture lending operations, while loan officers directly assist individual borrowers.
-
Customer interaction: Loan officers serve as the primary customer-facing representatives of lending institutions.
-
Loan approval: Lenders make final loan approval decisions, while loan officers collect documentation and make preliminary recommendations.
-
Loan options: Lenders establish their available loan programs, whereas loan officers educate borrowers on those set options.
-
Income source: Lenders earn interest income from mortgages, while loan officers earn commissions on originated loans.
While lenders establish loan options and make approval decisions, loan officers act as the face of the institution and shepherd borrowers through the mortgage process. Lenders provide the financing, but rely on loan officers to originate loans.
Which Should You Work With?
When it comes to getting a mortgage, you’ll need to interact with both lenders and loan officers. Here are some tips on working with each:
Loan officers
- Ask about the loan programs and rates offered by their lender
- Inquire about discounts or deals they can offer
- See if they have relationships with realtors or other industry professionals
- Evaluate their responsiveness and communication style
Lenders
- Compare interest rates and fees across multiple lender quotes
- Ask lenders about their loan options, credit requirements, and timelines
- Consider community banks, credit unions, or online lenders along with big banks
- Research lenders’ ratings and reviews from other borrowers
Understanding the role loan officers play as the face of the lending institution can help you have realistic expectations. Comparing multiple lenders helps find the best financing option for your needs.
The Bottom Line
While loan officers and lenders work together behind the scenes, their duties differ. Loan officers act as the representatives of lenders, guiding borrowers through the mortgage process. Lenders provide the financing, set loan options, and make approval decisions.
Knowing the key differences allows you to maximize your experience as a borrower. Loan officers simplify the complex mortgage process, while exploring multiple lenders helps you access the best loan programs and rates for your situation. With the right loan officer supporting your chosen lender, you can turn the dream of homeownership into reality.
Loan Officer
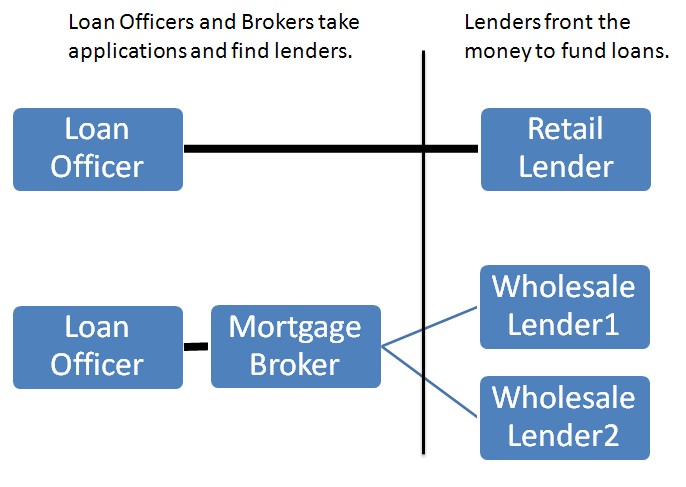
Loan officers represent the mortgage lender they work for and help borrowers apply for loans offered by the financial institution. Loan officers know the lending products, banking industry rules and regulations, and the required loan documentation to advise their clients.
Loan officers help guide borrowers based on their financial circumstances and assist with the mortgage process. They work with the lenders underwriter, who reviews the applicants creditworthiness and ability to pay the loan. When the loan is approved, the loan officer prepares the mortgage closing documents.
Some loan officers are compensated through commissions. This commission is a prepaid charge and is often negotiable. Commission fees are usually higher for mortgage loans than other types of loans. Large banks commonly work exclusively through their loan officers, and an independent mortgage broker will not offer their products.
Loan officers work for just one financial institution and can only offer loans from their employer. A borrowers options are limited to the company offerings.
What Is a Mortgage Loan Originator?
Mortgage brokers and loan officers are considered mortgage loan originators (MLOs) and meet strict federal requirements to help negotiate mortgage loans.
Loan Officer vs Mortgage Broker
FAQ
Are loan officer and lender the same?
What is the difference between a mortgage broker and a lender?
What is another name for a loan officer?
What is the difference between a mortgage broker and a loan originator?
What is the difference between a loan officer and a lender?
Loan officers are sometimes called mortgage consultants, mortgage loan originators, home loan consultants, and mortgage planners. Lenders are the ones who front the money to fund your loan. Lenders have various names based on how they acquire their clients and what they do with your loan after it is funded.
What is the difference between a mortgage broker and a loan officer?
In summary, loan officers work for a single financial institution and offer its loan products, while mortgage brokers are independent and can recommend the best fit for borrowers from various lenders .Choose
What does a loan officer do?
Loan officers are typically employed by lenders or mortgage brokers. They find new clients, counsel borrowers on how to choose the best mortgage, and fill out loan applications. They typically make their money through commissions on the loans. Loan officers can also be mortgage brokers if they also process and broker loans.
How do I compare mortgage offers from loan officers?
To compare multiple offers from loan officers, you’ll need to submit mortgage applications to different lenders in order to receive quotes from each one. How they get paid. Loan officers are employees of the lender, while mortgage brokers are independent of the mortgage company.
