Note from the Editor: This article’s content is solely based on the author’s opinions and suggestions. It might not have received approval from any of our network partners through reviews, commissions, or other means.
Due to its flexible qualification requirements, the FHA loan is a government-backed mortgage that is popular with first-time homebuyers and repeat buyers with financial blips in their credit histories. It might be simpler to be approved for an FHA loan than a conventional loan if you have less money saved for a down payment and a lower credit score.
Even so, there are some additional costs and rules associated with the FHA loan that you should be aware of before deciding that it’s the best option for you.
How Does LendingTree Get Paid?
Companies on this website pay LendingTree, and this pay may have an impact on where and how offers appear on this website (such as the order). Not all lenders, savings products, or loan options are offered by LendingTree in the market.
Note from the Editor: This article’s content is solely based on the author’s opinions and suggestions. It might not have received approval from any of our network partners through reviews, commissions, or other means.
Due to its flexible qualification requirements, the FHA loan is a government-backed mortgage that is popular with first-time homebuyers and repeat buyers with financial blips in their credit histories. It might be simpler to be approved for an FHA loan than a conventional loan if you have less money saved for a down payment and a lower credit score.
Even so, there are some additional costs and rules associated with the FHA loan that you should be aware of before deciding that it’s the best option for you.
What is an FHA loan?
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA), a government agency that adheres to lending guidelines established by the United S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). To guard your FHA-approved lender against losses if you stop making mortgage payments, you’ll pay two types of mortgage insurance.
To qualify for an FHA loan, you don’t have to be a first-time buyer, but you do need to have lived in the house you want to buy for at least a year as your primary residence. There are no income restrictions, unlike many other first-time homebuyer programs, giving higher-earners another home loan option if they don’t have the minimum 620 credit score needed for a conventional loan.
When choosing an FHA loan, homebuyers frequently find the following benefits:
What is the FHA?
The FHA was established in 1934 to provide U S. better lending options for buying a home. A 50% down payment was typical back then, so you needed to be able to afford a mortgage in three to five years.
Over time, the FHA loan program’s rules permitted borrowers to put down as little as 3 percent. 5% and pay off the loan over a 30-year term. Because borrowers pay mortgage insurance premiums to guard them against financial losses in the event of mortgage default, lenders were and are still willing to take on the risk of making FHA loans.
FHA loans function similarly to other home loan programs in most respects. You must demonstrate your ability to pay the down payment and closing costs, as well as meet the qualification requirements based on your income, credit history, and employment history. The minimal mortgage requirements, however, differ significantly from those of other loan programs.
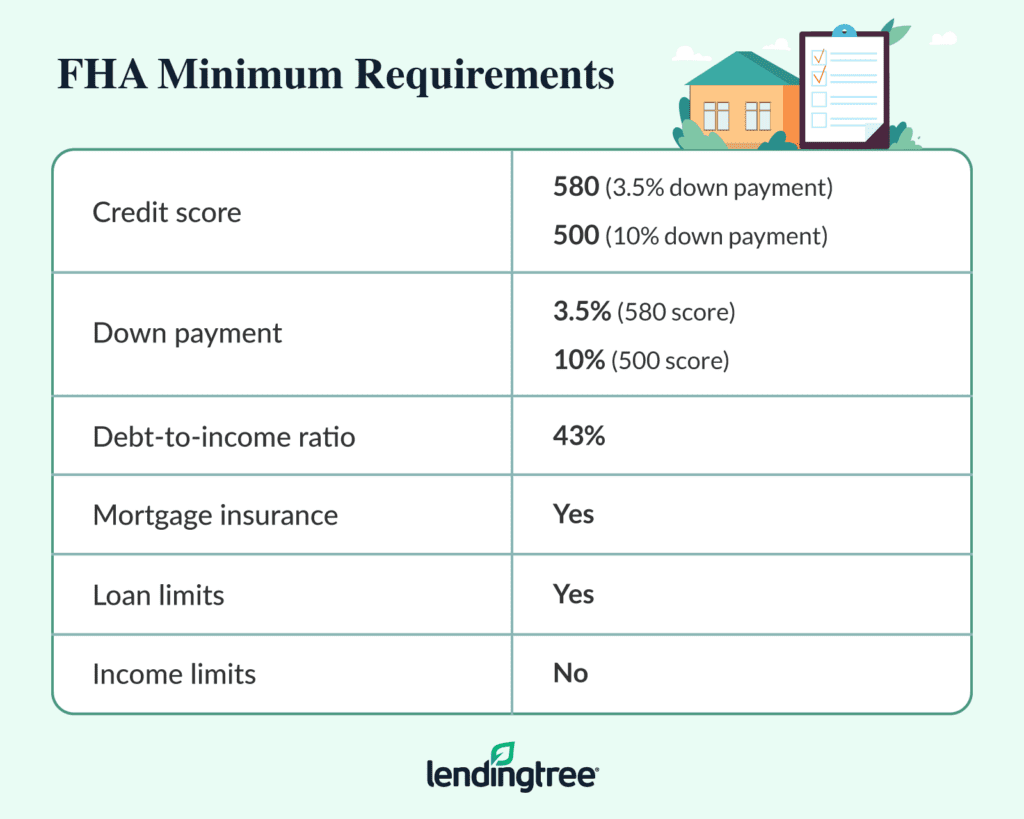
FHA loan down payment
To obtain an FHA loan, you’ll need to pay some money up front, including your down payment. The minimum amount you need depends on your credit score:
The good news is that you don’t need to save money on your own for the down payment. To raise the funds, you can ask a friend or relative for a gift, look into local down payment assistance (DPA) programs, or even sell an asset like a car.
FHA mortgage income requirements
Since there are no income restrictions to qualify for an FHA loan, you won’t have to worry about making too much money. Most of the traditional 3% down-payment programs that Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac offer are only available to homebuyers with low to moderate incomes.
You must have two years’ worth of pay stubs and W-2s to prove a consistent income history. Explain any significant gaps in your employment history.
FHA loan credit score and credit history
If their credit history has had a few blips, homebuyers frequently opt for FHA loans. The minimum credit score required by FHA regulations is lower than the conventional loan benchmark of 620:
In contrast to the stricter requirements of conventional lending, borrowers who have experienced significant credit events like bankruptcies or foreclosures also receive a break:
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
According to FHA regulations, lenders must check for any defaulted government-backed loans using the Credit Alert Interactive Verification Reporting System (CAIVRS). You may not be eligible for an FHA loan if you have defaulted on federal student loans, Small Business Administration (SBA) loans, prior VA loans, or prior USDA loans.
To determine whether you can afford your mortgage payment, lenders divide your total debt by your pre-tax income. Your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is what lenders refer to as, and FHA guidelines specify a preferred DTI ratio of 43%. If you have a high credit score and sufficient cash reserves, you may be eligible for a DTI ratio higher than 50%.
A requirement for mortgage cash reserves, which are funds set aside to cover a minimum number of monthly mortgage payments, may be triggered by a high DTI ratio or low credit scores. If you’re purchasing a multi-unit building and counting on the rent from the other units to help you qualify for a loan, you’ll need cash reserves.
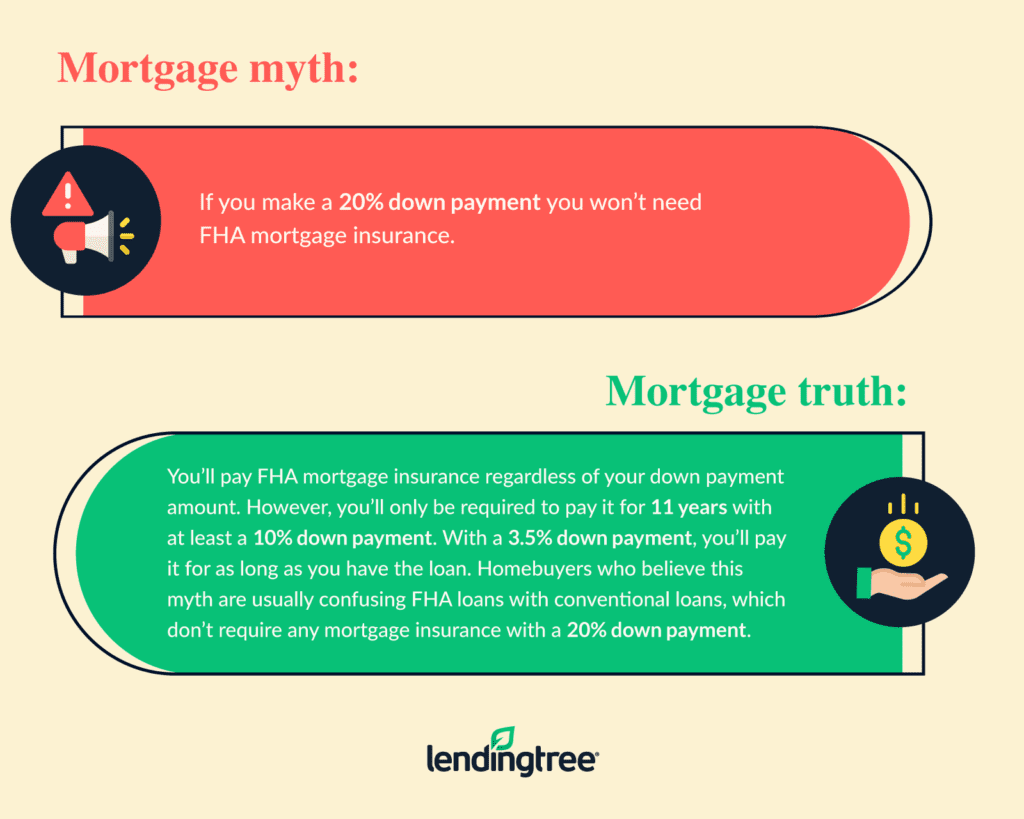
Each mortgage closed by an FHA-approved lender is covered by the FHA through an upfront and ongoing mortgage insurance premium. Mortgage insurance, in contrast to homeowners insurance, only pays the lender’s expenses if you are unable to make your monthly payments and the lender is forced to foreclose on your home.
Here is how and how much FHA mortgage insurance costs:
With a larger down payment, shorter loan term, or a smaller mortgage, you can lower the percentage of FHA insurance you pay each month. To experiment with various options and determine how they will affect your monthly payment, use an FHA mortgage calculator. Or even better, request loan estimates with various variations from your loan officer.
A percentage of the loan limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) is used by the FHA to determine new annual borrowing caps. Your county of residence determines the FHA loan limits, which may be higher in more expensive regions of the nation. If you’re purchasing a two to four-unit property, you’ll also have more borrowing power.
You can check the FHA mortgage limits website to find out the current limits in your area. The table below breaks down this year’s low-cost and high-cost area limits
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
You might want to look into the conforming loan limits in your area if FHA loan limits don’t provide you with enough money to make a purchase feasible. For instance, the FHA limit for a single-family home is $453,650 in most areas of the country, whereas the conforming conventional loan limit for a one-unit is $647,200.
FHA loan interest rates
Only lenders who have been approved by the FHA may offer FHA loan rates. This is crucial because not all mortgage companies offer FHA loans when you’re shopping. Like any mortgage rate, your rate will be better the higher your credit scores are.
Aim to improve your credit whenever possible before applying for an FHA loan. Any of the following could raise your credit scores and enable you to get a better deal:
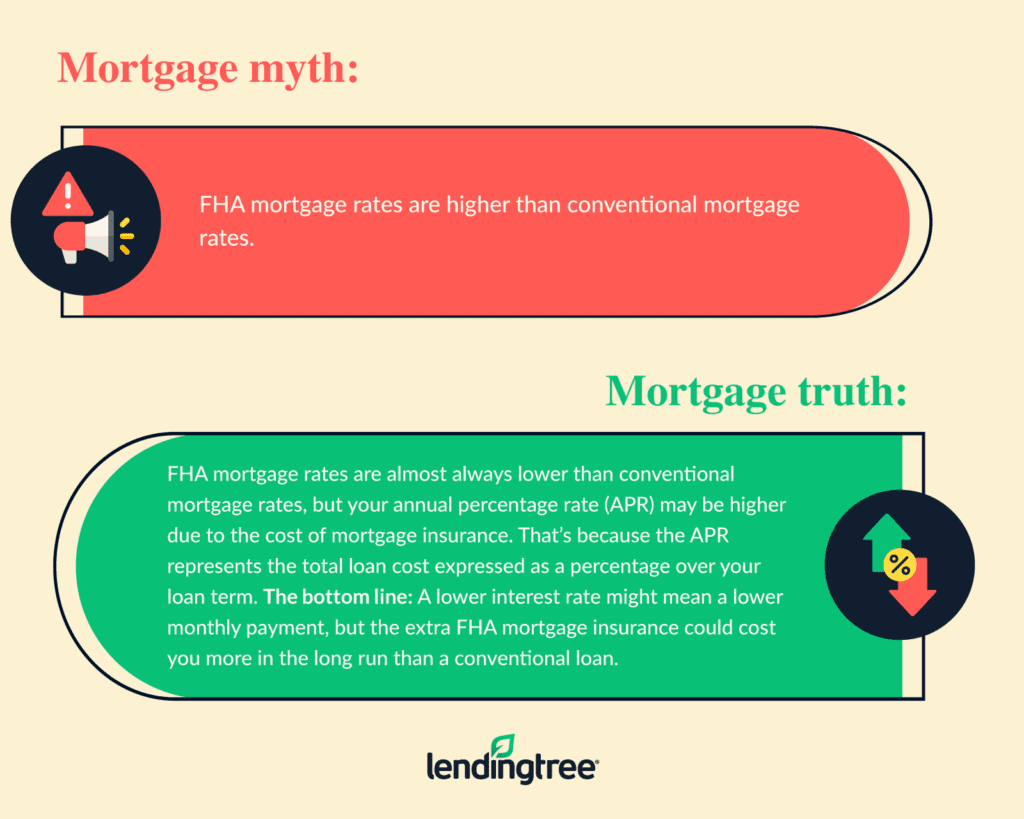
Between 2% and 6% of your loan amount should go toward FHA closing costs. Other than mortgage insurance, there are some closing costs specific to FHA loans.
Different types of FHA loans
In order to meet the needs of homebuyers and homeowners throughout their financial lives, the FHA provides a variety of different loan programs.
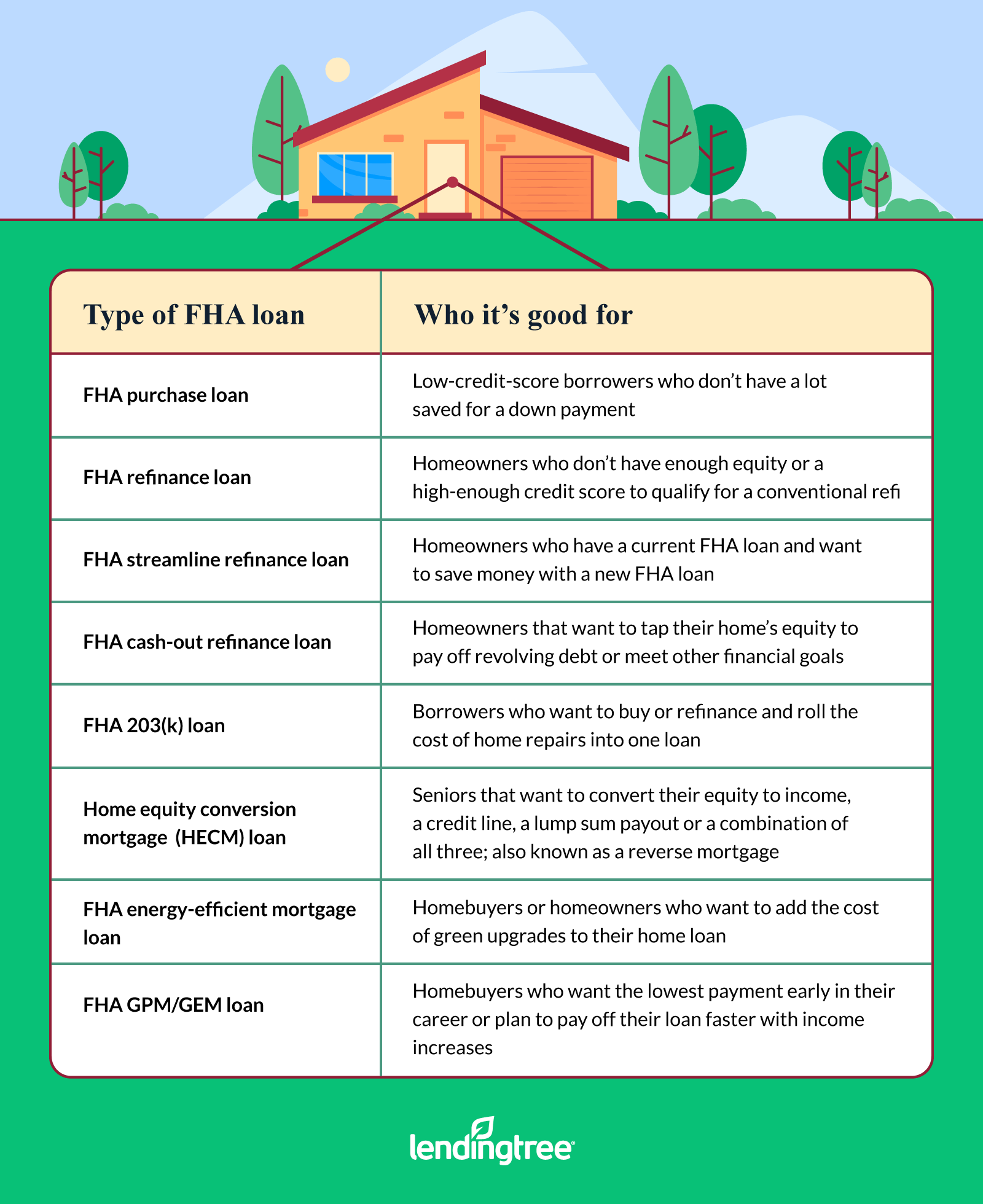
The majority of buyers of homes opt for a “standard” FHA loan. This type of FHA loan, also known as the 203(b) program, offers the flexibility in down payment and credit score requirements we discussed above.
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
No prospective homeowner wants to spend more money on a home than it is worth, and the FHA ensures that you have a plan of escape through the FHA amendatory clause. It’s necessary if you’re making an offer on a home financed by an FHA loan and gives you the option to back out of the deal and get your earnest money back if the value of the property differs from the sales price.
Replace your existing loan with a new FHA loan of up to 97 percent. 75% of your home’s value. You must have a minimum credit score of 580 and may include your FHA closing costs in the loan amount. This is more commonly known as a “rate-and-term” refinance.
FHA streamline refinance loan
Homeowners who currently have an FHA loan may be eligible for an FHA streamline refinance, which lowers their monthly payment. The process is very simple because you can omit the income documentation and there is no need for a home appraisal.
FHA cash-out refinance loan
With an FHA cash-out refinance, borrowers with credit scores as low as 500 might be able to borrow more money than they currently owe and keep the difference in their pockets. But with this choice, you’re limited to borrowing no more than 80% of the value of your house.
FHA 203(k) renovation loan
With the 203(k) mortgage program, you can buy or refinance a home and combine the costs of renovation into a single loan. For smaller projects (under $35,000), you can select the limited program, whereas the standard program offers more funding for bigger projects.
Home equity conversion mortgage (HECM)
The HECM loan, also known as a reverse mortgage, offers borrowers aged 62 or older a variety of ways to convert their home equity into cash and forego a monthly payment. The borrower typically needs to have at least 50% equity in their home to qualify. The age of the youngest homeowner determines the amount of equity that is available.
With this program, which is referred to as an EEM in short, you can add the cost of energy-saving upgrades to the balance of a loan for a purchase or refinance. You might be able to obtain an FHA EEM loan for between $1,500 and $25,000 depending on the type of improvements you make.
With a graduated payment mortgage (GPM), borrowers can select lower initial monthly payments that rise in line with their rising income. The growing equity mortgage (GEM) allows borrowers who want to pay off their mortgage faster to make additional payments toward the loan balance.
FHA loans vs. conventional loans
Frequently, credit scores and overall debt determine whether a borrower chooses an FHA loan or a conventional mortgage. The most common type of mortgage is a conventional loan, but applicants must meet stricter requirements than for FHA loans.
But with conventional loans, you can finance second homes and investment properties, whereas with an FHA mortgage, you have to live in the house you finance for at least a year as your primary residence. Additionally, if you use a conventional loan to purchase a home, you might be eligible for an appraisal waiver, whereas FHA purchase loans call for a more thorough home appraisal.
The key differences between FHA and conventional loans are highlighted in the table below.
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
If you don’t have a 20% down payment and your credit scores are above 620, you may want to compare the cost of FHA mortgage insurance to conventional private mortgage insurance (PMI). FHA MI premiums are not based on credit scores, in contrast to conventional PMI premiums, which could have a significant impact on your monthly payment and your ability to borrow more money.
How to apply for an FHA loan
With a few exceptions, applying for an FHA loan is generally similar to applying for any other kind of home loan. Here are the first six steps to applying for an FHA loan.
Questions to ask your loan officer about FHA loans
Not all loan officers are familiar with the FHA loan program, a specialized government loan program. When you’re shopping, it’s worth it to inquire about lenders who have stricter requirements than the FHA.
Pros and cons of FHA loans
The benefit of FHA loans is that they allow for much lower credit scores than conventional loans do, as well as down payments as low as 3.5%. 5% of the home’s price. You might even be preapproved with a DTI ratio higher than 50% if you have a few extra dollars in the bank and a better credit score.
One disadvantage of FHA financing is the additional cost of mortgage insurance. Due to the lower maximum loan limits than conventional loans, an FHA loan may not make sense if you reside in a region of the country where home prices are high. Here’s a brief recap of FHA loan pros and cons.
As long as they apply through a lender that has received approval from the FHA, any borrower who satisfies the FHA loan requirements may be eligible.
PMI doesn’t apply to FHA loans. Instead, borrowers make one lump-sum payment for the upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP). 75 percent of the total amount of your loan and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP) between 0 and 45% and 1. 5% of the total loan balance, divided by 12, plus the monthly payment
The official program code for the standard program for FHA purchase and refinance loans is FHA 203(b).
Yes. Aspiring homeowners can now apply for a mortgage with student loan debt and qualify based on their actual student loan payment thanks to recent changes to FHA guidelines. Before the modification, which became effective in the summer of 2021, FHA-approved lenders had to determine the student loan balance at 1% in order to be eligible, regardless of whether the actual payment was lower.
Yes. Lenders that are FHA-approved may preapprove you for an FHA loan after examining your income, cash for the down payment, credit score, and payment history.
In most cases, getting an FHA loan is simpler than getting a conventional loan. Because of the flexible requirements of the FHA loan program, borrowers with less-than-perfect credit and little savings can own a home and build wealth and a stable foundation for their families.
After putting down 10% for an FHA loan, you have a choice of waiting 11 years or switching to a conventional loan. Only conventional loans provide various ways to do away with mortgage insurance.
The maximum amount you can obtain from an FHA loan is based on three factors.
For the most accurate estimate of the amount of the FHA loan you are eligible for, it is best to get preapproved with a loan officer.
Compare FHA Loans for Free Loan type:
Learn about the various mortgage loan types, including conventional loans and government-backed FHA, VA, and USDA loans, so you can make the best decision.
If you have a great house hunting checklist, you might be able to get the home you want instead of losing out to someone who was more prepared.
If you don’t have enough money for a down payment to buy a home, find out how a down payment assistance program can help.
FAQ
What are the benefits of an FHA loan?
- Easier Credit Qualifications. …
- Shorter Time After Negative Credit. …
- Low FHA Loan Down Payment. …
- More Lenient on Gift Funds. …
- Some Closing Costs Can be Financed. …
- Seller Paid Closing Costs Save Borrower. …
- More Affordable Mortgage Insurance. …
- Higher Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
What is the downside of an FHA loan?
FHA loans will likely have higher costs upfront and with each payment, which may indicate that borrowers aren’t ready for a mortgage. Mortgage insurance is also required, and FHA loans are less flexible than conventional loans.
What is the greatest advantage of using FHA?
Reduced Credit Score and Down Payment Requirements Because an FHA loan is backed by the government, they are less stringent than those for conventional loans. A minimum credit score of 580 and a 3 percent down payment are needed for buyers. 5% to qualify.
Is conventional or FHA better?
If you have good or excellent credit, a conventional loan is frequently preferable because it will result in lower mortgage rates and PMI costs. However, if your credit score is in the high 500s or low 600s, an FHA loan may be the best option. For lower-credit borrowers, FHA is often the cheaper option.
