A 40-year mortgage is like a traditional 15- or 30-year mortgage, but it offers an extended repayment term. Having ten more years to pay off a loan can give you lower monthly payments, but in the long term you’ll pay far more interest.
40-year mortgages can be a more affordable way to purchase a home in today’s increasingly expensive housing market, but that’s not the most common way they’re used. More often, lenders modify an existing loan’s repayment term to 40 years in order to help struggling homeowners avoid foreclosure.
A 40 year house loan may seem unusual compared to the standard 15 or 30 year mortgage but it can be a viable option for some homebuyers. With housing affordability decreasing across the nation, more first-time buyers are looking into extended loan terms to make homeownership possible.
While 40 year mortgages come with pros and cons, they allow borrowers to take advantage of lower monthly payments. We’ll break down how these extended loans work, who offers them, eligibility requirements, interest rates, and alternatives to consider
What is a 40 Year Mortgage?
A 40 year mortgage is simply a home loan with a 40 year repayment term. The borrower makes 360 monthly payments over 40 years to pay off the entire loan amount and interest These loans help increase affordability since the payments are spread out over a longer timeline.
Most conventional mortgages have either a 15 or 30 year term. VA and USDA loans sometimes offer terms extending out to 40 years. The 40 year option isn’t as widely available, but some lenders do provide this extended alternative.
These loans come in a few different structures:
-
Fixed-rate – The interest rate stays the same for the full 40 years.
-
Adjustable-rate (ARM) – The rate starts fixed for 5-10 years then adjusts periodically.
-
Interest-only – You only pay the interest for the first portion of the loan, then principal + interest.
-
Balloon mortgage – Payments are lower except for a large balloon payment at the end.
Who Offers 40 Year Mortgages?
Since they are less common, 40 year mortgages aren’t offered by every lender. Large banks tend to only provide 15 and 30 year loan options. Here are some places that may offer 40 year mortgages:
- Small local lenders
- Credit unions
- Online lenders
- Mortgage brokers
Some specific lenders known for 40 year loan programs include Newrez, Carrington Mortgage Services, and Needham Bank. Even if a lender doesn’t advertise this term length, it can’t hurt to ask them about it.
VA and USDA loans guaranteed by government agencies are most likely to provide 40 year mortgage choices.
Pros and Cons of 40 Year Loans
Before committing to a longer repayment timeline, weigh the key pros and cons:
Pros
-
Lower monthly payments – Spreading the payments over 40 years instead of 30 years reduces the monthly costs. This helps first-time homebuyers qualify for a higher loan amount.
-
Increased buying power – You may be able to afford a more expensive house with a 40 year term and the lower payments.
-
Build equity slower – While less equity is built at first, you still gain some each month and will eventually have 100% equity after 40 years.
-
Interest-only flexibility – Some 40 year loans offer interest-only periods which provide payment flexibility.
Cons
-
Higher interest rates – 40 year mortgages often come with a slightly higher rate than 30 year loans.
-
Difficult to find – Not all lenders offer this extended term length.
-
More interest paid – You’ll pay significantly more interest over the full 40 years compared to a shorter term.
-
Less equity built early – Equity grows slower over 40 years vs. 30 years. This can limit options later to tap equity or sell.
Overall, the lower monthly payments provide the main benefit to offset the higher long-term costs.
40 Year Mortgage Eligibility and Requirements
Since 40 year mortgages are considered riskier by lenders, they have more flexible qualification requirements than conventional 15 or 30 year loans. Here are some typical eligibility standards:
-
Credit score – Minimum scores range from 580 to 640. Some lenders may go lower.
-
Down payment – 5-10% is commonly required. Certain loans allow 3-5%.
-
Debt-to-income ratio – Many lenders require max DTI of 50%. Some allow higher.
-
Home value limits – Loan amounts are capped based on home value. Limits range from around $550k up to $2.5M.
-
Location – Not limited to specific areas, but availability can vary by state and region.
Always verify specific requirements with individual lenders, as their standards can differ. VA and USDA loans will also have their own eligibility criteria.
40 Year Mortgage Rates
Interest rates on 40 year loans tend to run 0.25% to 0.75% higher than comparable 30 year fixed rates. This premium reflects the added risk and cost associated with the longer repayment term.
Here are some sample 40 year fixed rate mortgage ranges:
-
Excellent credit – 6.25% to 6.75%
-
Good credit – 6.75% to 7.25%
-
Fair/poor credit – 7.5% to 8.5%
Actual rates you’re offered will depend on your individual credit score and history along with current market rate trends. Get rate quotes from multiple lenders to find your best option.
How to Get a 40 Year Mortgage
If you want to apply for a 40 year purchase mortgage, the process is similar to other home loans:
-
Compare mortgage rates and lenders to choose options. Credit unions, small banks, and non-bank lenders are good prospects.
-
Get pre-approved for an amount you’re comfortable borrowing.
-
Make an offer on a home and apply for financing if your offer is accepted.
-
Provide documents to verify income, savings, and assets to your lender.
-
Complete the home appraisal, underwriting, and closing process.
During underwriting, be prepared to explain why the 40 year term makes sense for your situation. A mortgage broker can also guide you through the steps and identify lenders to try.
Alternatives to Consider
While a 40 year mortgage provides lower payments, you may want to consider these other options too:
-
30-year mortgage – With today’s rates, a 30-year loan could still be affordable. Get quotes to check.
-
Adjustable-rate mortgage – An ARM starts with a fixed rate for 5-10 years. Payments increase after it becomes adjustable.
-
FHA, VA, or USDA loans – Government-backed programs offer competitive rates and more flexible requirements.
-
Mortgage points – You can pay points upfront to lower your interest rate on a 30-year loan. This cuts payments without extending the term.
-
Buy down mortgage rate – Similar to points, you pay a fee to the lender to get a discounted rate for 1-3 years.
Run the numbers on these alternatives or combinations of strategies. A shorter term or lower rate could work better overall.
The Bottom Line
While uncommon, 40 year mortgages serve an important role in helping first-time buyers afford a home. The lower payments provide flexibility, but also come with higher long-term costs.
Weigh the pros and cons carefully and get rate quotes from several lenders. Be sure you understand the risks before committing to pay off a mortgage over 40 years. With proper budgeting, a 30-year term may still fit your needs at an affordable payment.
How to get a 40-year mortgage
The process to get a 40-year mortgage at the time of purchase (not as a loan modification) is very similar to what you’d do to get a 30- or 15-year loan. But there are a few differences to keep in mind:
- The minimum requirements to qualify vary. Nonqualified mortgages don’t have the same minimum mortgage requirements as traditional loans and they can vary from lender to lender. Non-QM lenders have wide leeway to decide what minimum credit scores, loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and debt-to-income (DTI) ratios they will accept.
- There are limited lenders you can choose from. Because 40-year purchase loans aren’t widely available, you may need to do some extra research or go through a mortgage broker to find a lender. But before settling on one, make sure you’re working with a reputable lender. Most legitimate lenders are listed in the NMLS loan originator database.
![]()
How does a 40-year mortgage compare to a 30-year mortgage?
A 40-year mortgage can lower your monthly payments, but it’ll also greatly increase how much you’ll pay in interest. To see what this could look like in the real world, choose the example below that applies to your situation. If you’re only interested in how a longer loan term can affect your ability to build home equity, head to the final example.
Below, we compare two hypothetical loan options for a $430,000 home with a 13% down payment. As a best-case scenario, we’ll give both loans the same interest rate.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Monthly payment | Total cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-year mortgage | $374,100.00 | 7.79% | $2,690.45 | $968,560.64 |
| 40-year mortgage | 374,100.00 | 7.79% | $2,542.39 | $1,220,346.21 |
Takeaways: While you’d save $148.06 per month on your mortgage payments by going with a 40-year loan, you would end up spending about $251,800 more for the privilege.
Here we look at both 30- and 40-year loan options for a home with $300,000 still owed to the lender. In our example, there is no difference in the interest rate because a loan modification doesn’t alter the interest rate of the existing loan. The monthly payment amounts reflect principal and interest only.
| Loan amount | Interest rate | Monthly payment | Total cost | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30-year mortgage | $300,000.00 | 6.27% | $1,851.06 | $666,380.04 |
| 40-year mortgage | $300,000.00 | 6.27% | $1,707.45 | $819,576.04 |
Takeaways: In this example, you would have paid $153,196 more in interest by choosing to modify your loan. But, on the other hand, if this was the only way to prevent foreclosure, it may very well have been worth it.
It’s worth taking a look at how much more slowly you’ll build equity with a 40-year loan, because it can affect your ability to get other loans or sell your home in the future. The chart below compares the equity-building timelines for 30- and 40-year mortgages.
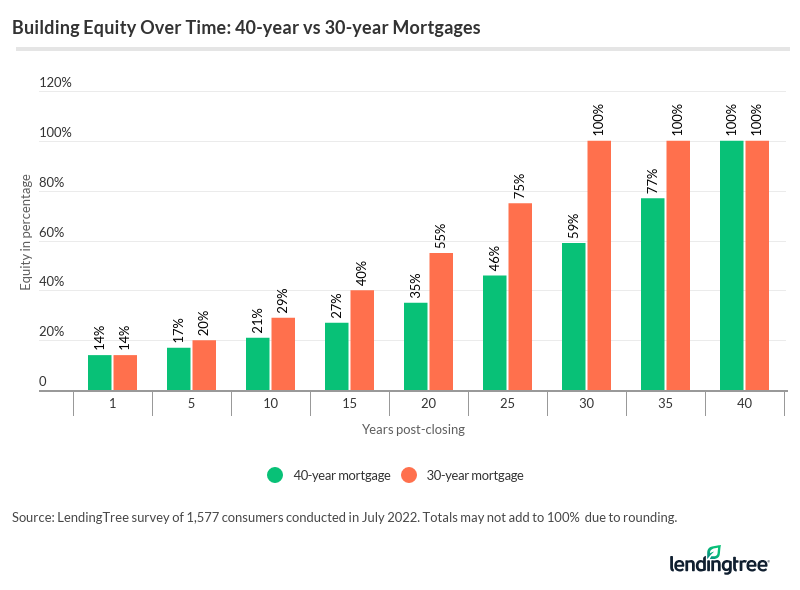
As you can see, with a 30-year loan, you would build 20% equity in just five years — but with a 40-year loan, you’d have to wait nearly nine years to build that much equity. And depending on other terms of the loan (e.g., an interest-only period), it could take even longer to build equity.
The (shocking) Truth Behind 40 Year Mortgages
FAQ
Is a 40 year mortgage available?
Is there a such thing as a 50-year mortgage loan?
Does Chase offer 40 year mortgages?
Is there a 40 year VA loan?
What is a 40 year mortgage?
A 40-year mortgage allows you to repay your loan over 40 years instead of the more common 30 or 15 years. This extended term comes with a lower monthly payment, but at the cost of a higher interest rate and more paid toward interest over the life of the loan. Forty-year mortgages are a type of non-qualified mortgage (non-QM loan), however.
Should I get a 40 year mortgage?
It depends on your financial goals. If you need a lower monthly payment, a 40-year mortgage can help, but it will mean paying significantly more in interest over time. If you want lower total costs by the end of your loan term, a shorter-term loan is a better option. Is it hard to qualify for a 40-year mortgage?
What is a 40-year fixed loan?
Similar to the common 30-year fixed loan, a 40-year fixed loan allows you to amortize the loan an additional 10 years so that you are paying off your loan over a 40-year time period. In this article: What is a 40-Year Fixed Mortgage? What is a 40-Year Fixed Mortgage?
How long does a 40 year home loan last?
Traditionally, mortgages come in loans anywhere between 8 – 30 years. In some cases, 40-year loans may have other features. For example, there might be interest-only periods for a certain timeframe at the beginning of the loan before switching to payments of principal and interest for the remainder of the term. How Does A 40-Year Home Loan Work?
